GH joint stability
동적요소
|
Active |
|
Compression of joint surfaces |
|
Dynamic ligament tension |
|
N-M control |
정적요소
|
Passive |
|
Joint geometry |
|
Adhesion/cohesion |
|
Ligamentous restraints |
|
Soft tissue barrier |
|
Glenoid labrum |
only 25~30% of the humeral head is in contact with the glenoid fossa.
Dynamic factors

●Rotator cuff
▷increase joint stability
▷increase joint compression
▷steering
Function of rotator cuff

Relationship of supraspinatus & deltoid muscle
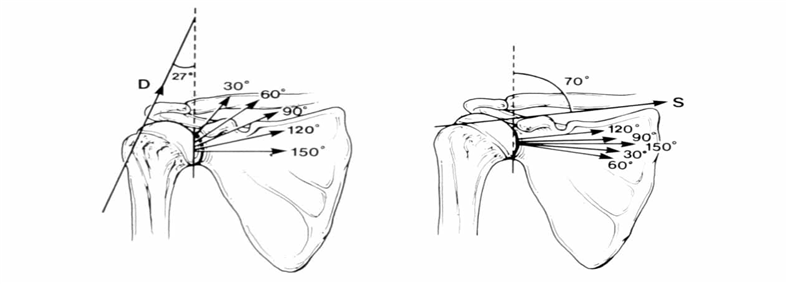
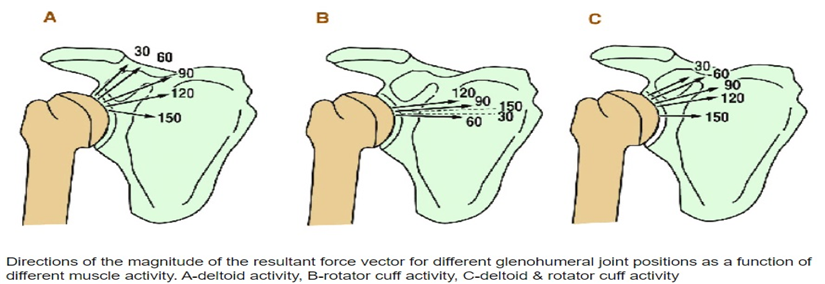
Force coupling compression force
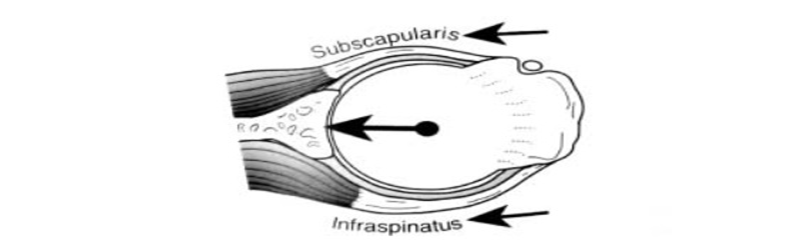
● Controlling shoulder motion and stability
● Reduce anterior translation
Biceps long head

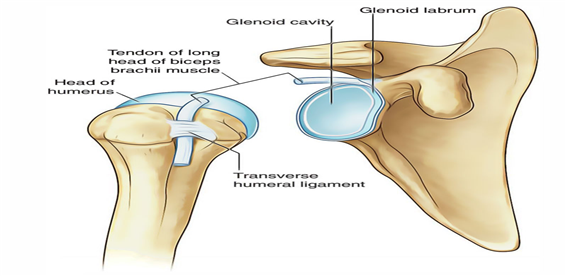
● Attach on the anterior, superior glenoid
● Contraction of biceps
▷ Decrease in superior & anterior translation
※ GIRD
GH joint biomechanics
First 30~60° scapular plane elevation: 1-3mm superior translation
30~60° lying supine abduction: 0.7mm inferior translation
not similarly recruit muscle activity
During passive glenohumeral motion, limited evidence demonstrates that during 30~60° superior translation occurs
GH joint 운동형상학(kinematics)
First 30~60° at scapular plane
0.7~2.7mm anterior translation
60~90°
0~1.5mm posterior translation
90~120°
1~4.5mm posterior translation
▶ Exernal rotation is important for clearance of the greater tuberosity during elevation
Effect of external rotation during elevation

▷increase humeral external rotation at scapular plane than sagittal and coronal plane.
▷Exernal rotation
its associated tissues as it passes under the coracoacromial arch
Effect of humeral ER

GH Joint Kinematics

● Subscapularis teres minor, infraspinatus contribute to depression of the humeral in the glenoid cavity more than does the supraspinatus. And/or provides dynamic stability to the GH joint during deltoid activation.
Subacromial space
● Height of the subaromial space
▷ 1~1.5cm
● At 90 elevation(healthy)
▷ 4.1mm
● Shoulder impingement
▷ 1.4mm
⇒ 6mm Superior displacement of humeral head if rotator cuff tear space effect
출처
Myers, Joseph B. shoulder muscle reflex latencies under various levels of muscle contraction. Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research. 407:92-101, February 2003.
Frederick A. Matsen, III, Caroline Chebli and Steven Lippitt. Principles for the Evaluation and Management of Shoulder Instability. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:647-659.
Morrey BF, An KN (1990) Biomechanics of the shoulder. In: Rockwood CR, Matsen FA (ed) The shoulder. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 208–245Google Scholar.
Philip Mcclure, Lori A. Michener. Direct 3-dimensional measurement of scapular kinematics during dynamic movements in vivo. Published in Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery 2001
Parsons IM1, Apreleva M, Fu FH, Woo SL. The effect of rotator cuff tears on reaction forces at the glenohumeral joint. J Orthop Res. 2002 May;20(3):439-46.
Young Jin Jo1, Young Kyun Kim. Consideration of Shoulder Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation Exercise for Overhead Sports Population. Asian J Kinesiol 2019; 21(2): 40-50 · DOI: https://doi.org/10.15758/ajk.2019.21.2.40
Ofer Levy, Hannan Mullett, The role of anterior deltoid reeducation in patients with massive irreparable degenerative rotator cuff tears. Medicine Published in Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery2005 DOI:10.1016/j.jse.2008.04.005
https://www.hep2go.com/index_b.php?userRef=120148
'물리치료 공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 어깨(회전근개) 수술후 재활 part 6(Rotator cuff tear repair Protocol Phase1 (1~4weeks)) (0) | 2020.08.30 |
|---|---|
| 어깨(회전근개) 수술후 재활 part 5(Rotator cuff tear repair) (0) | 2020.08.29 |
| 어깨(회전근개) 수술후 재활 part 3 (Rotator cuff 소개) (0) | 2020.08.28 |
| 어깨(회전근개) 수술후 재활 part 2(Glenohumeral Joint 의 정의 ) (0) | 2020.08.27 |
| 어깨(회전근개) 수술후 재활 part 1 서론 (0) | 2020.08.27 |