이번에는 코어 운동에 대해서 게시하겠습니다.
Core exercise
Breathing
-breathing has on core stability and chronic neck and shoulder pain
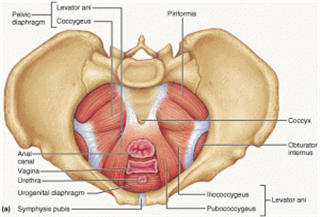
-current literature suggests that the diaphragm, transversus abdominis, multifidius and pelvic floor work in unison to create the ideal intra-abodminal pressure for spinal stabilization
-these “inner core” muscles fire in an anticipatory manner milliseconds before the prime movers in an effort to stabilize the spine at the segmental level
High – low breathing

-Ideally, the hand on the belly should rise before the hand on the chest.
-The hand on the chest should move slightly forward (not toward the chin)
-If it moves significantly more than the hand on the abdomen, there is a suggestion of dysfunctional breathing
Breathing exercise


Diaphragm test(lateral expansion)

Both the fingers and thumbs should be moving apart form each other, ideally 1.5-2 inches apart
Bracing maneuver
-This is the practice of activating muscles surrounding the trunk in order to protect the spine, safely transfer power between upper and lower body, and stand ground against contact.
-Breathe in and out. Gently and slowly push out your waist without drawing your abdomen inward or moving your back or pelvis.
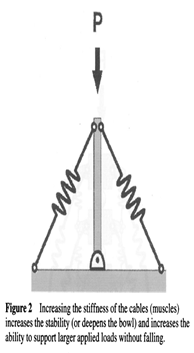


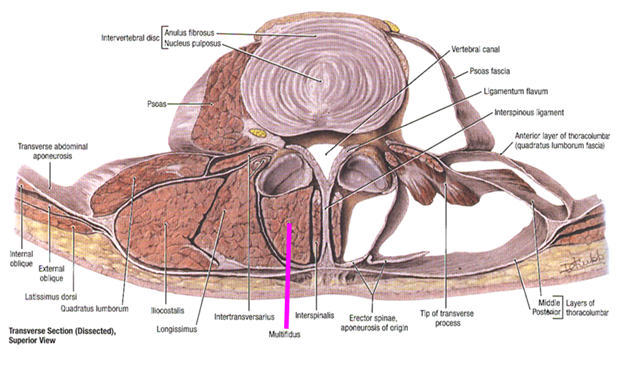
As multifidii contract, it pushes into the thoracolumbar fascia and along with contraction of the transversus abdominis, provides intersegmental stability.

a) The relaxed multifidi muscle in transverse section; b) Co-contraction of the transversus abdominis and multifidi creates a stiffening tension on the thoracolumbar fascia thereby providing intersegmental stability.
Bracing exersise
This is the practice of activating muscles surrounding the trunk in order to protect the spine, safely transfer power between upper and lower body, and stand ground against contact.
bracing + moment arm (UE>LE) >> theraband >> change of posture


supine bracing


1. Supine Core Bracing
2. Supine Core Bracing with Arms Extended Toward Floor
3. Supine Core Bracing with One Leg Up (hold 10-15 seconds each side)
4. Supine Core Bracing with One Leg Up and Arms Extended Toward Floor
5. Band Resisted Supine Core Bracing
6. Partner Resisted Supine Core Bracing
DEAD BUG (+ bracing)


1. Dead Bug
2. Dead Bug with Arms Extended Toward Floor
3. Dead Bug with One Leg Toward Floor
4. Dead Bug with Opposite Arm and Leg Toward Floor
5. Band Resisted Dead Bug
6. Partner Resisted Dead Bug
SIDE PLANK


PALLOF PRESS

SUPER HERO and HALF-AIRPLANE (from hands and knees or stability ball)



Caution during breathing
Co-activation of the multifidus
Common substitution patterns or faults
asymmetry of contraction
breath-holding
bracing and increasing intra-abdominal pressure with overactivation of the abdominal muscles
results in movement of the trunk or pelvis out of a neutral position, and into spinal flexion or posterior tilt.
Reference
co-activation of muscle in spinal column craig 2004
kibler et al. sports med 2003
Mcgill. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 2001
Paul Hodge. Intervertebral Stiffness of the Spine Is Increased byEvoked Contraction of Transversus Abdominis and theDiaphragm:In VivoPorcine Studies
Musculoskeletal Evidence based Treatment
Paul W. Hodges. 1.5 Low Back Pain and the Pelvic Floor
Jessica Reale, PT Yoga Anatomy: 6 Reasons Why the Diaphragm May Be the Coolest Muscle in the Body
faries&greenwood. streng & condit j 2007
C. Frank, A. Kobesová, P. Kolář Published 2013 Medicine International journal of sports physical therapy Dynamic neuromuscular stabilization & sports rehabilitation.
Sapsford RR, Hodges PW, Richardson CA, Cooper DH, Markwell SJ, Jull GA. Co-activation of the abdominal and pelvic floor muscles during voluntary exercises. Neurourol Urodyn. 2001;20(1):31-42. doi: 10.1002/1520-6777(2001)20:1<31::aid-nau5>3.0.co;2-p. PMID: 11135380.
Arnold Fomo on Aug 23, 2018 Trigger Point Therapy - Understanding and Treating Multifidus
McGill, PhD J Can Chiropr Assoc 1999 (Jun); 43 (2): 75–88 ~ FULL TEXT Stability: from biomechanical concept to chiropractic practice
Leon Turetsky (NASM-CPT, NASM-CES), Last Updated: March 5, 2020 Abdominal Bracing VS Drawing In – For Core Exercises
Kristen Gostomski, B.S. Sports & Health Science, HSSCS, INHC Best and Worst Core Exercises for Athletes
https://youthsportstrainer.com/
https://www.muscleandmotion.com/abdominal-bracing/
https://youthsportstrainer.com/best-and-worst-core-exercises-for-athletes/
'물리치료 공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 4. Impingement Syndrome의 이학적 검사 (0) | 2022.01.06 |
|---|---|
| Impingement Syndrome의 정의 (0) | 2022.01.02 |
| Core (0) | 2020.10.18 |
| 척추전방전위증(Spondylolisthesis) (0) | 2020.10.04 |
| 어깨(회전근개) 수술후 재활 part 6(Rotator cuff tear repair Protocol Phase4 (12~16weeks)) (0) | 2020.09.07 |