Core


Abdominals in the front, paraspinals and gluteals in the back, the diaphragm as the roof, and the pelvic floor and hip girdle musculature as the bottom
The core is particularly important in sports because it provides "proximal stability for distal mobility".

* Provide mechanical stability of spine
* Increase functional mobility (N-M control)
* Decrease pain
Spinal stability
spinal stability is a prerequisite element that enables movement of the limbs by maintaining the spine upright in postural changes
Innor core – TRA, Diaphragm, Pelvic floor musculature, MF
TRA
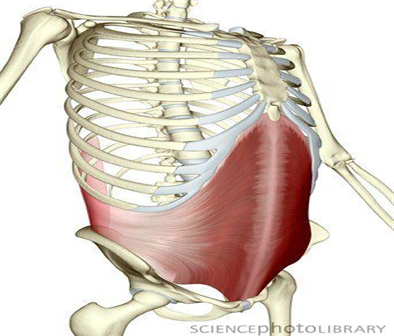
The transversus abdominis has large attachments to the middle and posterior layers of the thoracolumbar fascia
Thoraco-lumbar fascia, provides a connection between the lower limb and the upper limb
Thoraco-lumbar fascia also functions as a proprioceptor, providing feedback about trunk positioning
Creating a belt around the abdomen. “hollowing in” of the abdomen creates isolated activation of the transversus abdominis
The transversus abdominis and multifidius habe been shown to contract 30ms before movement of the U/E and 110ms before movement of the L/E in healthy people
Theoretically to stabilize the lumbar spine
Delayed activation of transversus abdominis in patients with low back pain may be more related to the lack of trunk rotation used in the arm raise by these subjects
Re-establishes a normal asymmetrical transversus abdominis action during rotation tasks within a complex muscle synergy rather than correcting a single dysfunctional muscle.
Paul Hodge 실험


Electrical stimulation of the diaphragm increased IAP without abdominal or paraspincal activity
IAP produces an extensor moment.
IAP may influence intervertebral stiffness directly by tensioning the spine or indirectly by increasing the hoop tension in the abdominal muscles and their fascias.
Diaphragm

Contraction of the diaphragm increases intra-abdominal pressure, thus adding to spinal stability.
Abnormal position and recruitment of the diaphragm resulted in subsequent reduced intra-abdominal pressure conducive to low back pain


Pelvic floor musculature
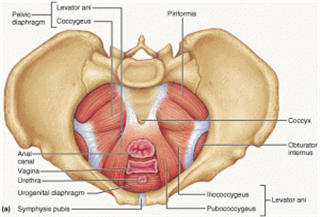

Pelvic floor musculature is co-activated with transversus avdominis contraction
people with sacroiliac pain have impaired recruitment of the diaphragm and pelvic floor.

Abdominal muscle activity is a normal response th PF exercise in subjects with no symptoms of PF muscle dysfunction and provide preliminary evidence that specific abdominal exercises activate the PF muscles
in healthy subjects, voluntary activity in the abdominal muscles results in increased pelvic floor muscle activity
The increase in pelvic floor pressure before the increase in the abdomen pressure indicates that this response is preprogrammed

The diaphragm, pelvic floor and transversus abdominis regulate IAP and provide anterior lumbo-pelvic postural stability.
Multifidus

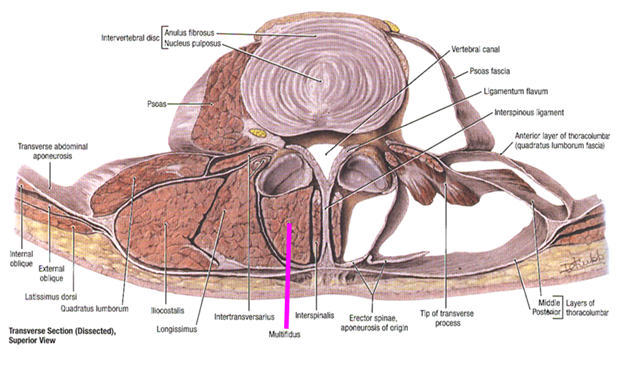
Multifidus attachment to the spinous process, the multifidus has a longer lever arm for producing extension than do the erector spinea muscles that attach to the transverse process
The most important action of the multifidus is controlling the flexion and anterior shear of the spine during forward bending via its eccentric contraction
Reference
Musculoskeletal Evidence based Treatment
co-activation of muscle in spinal column craig 2004
kibler et al. sports med 2003
Mcgill. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 2001
Paul Hodge. Intervertebral Stiffness of the Spine Is Increased byEvoked Contraction of Transversus Abdominis and theDiaphragm:In VivoPorcine Studies
Paul W. Hodges. 1.5 Low Back Pain and the Pelvic Floor
Jessica Reale, PT Yoga Anatomy: 6 Reasons Why the Diaphragm May Be the Coolest Muscle in the Body
faries&greenwood. streng & condit j 2007
C. Frank, A. Kobesová, P. Kolář Published 2013 Medicine International journal of sports physical therapy Dynamic neuromuscular stabilization & sports rehabilitation.
Sapsford RR, Hodges PW, Richardson CA, Cooper DH, Markwell SJ, Jull GA. Co-activation of the abdominal and pelvic floor muscles during voluntary exercises. Neurourol Urodyn. 2001;20(1):31-42. doi: 10.1002/1520-6777(2001)20:1<31::aid-nau5>3.0.co;2-p. PMID: 11135380.
Arnold Fomo on Aug 23, 2018 Trigger Point Therapy - Understanding and Treating Multifidus
Musculoskeletal Evidence based Treatment
McGill, PhD J Can Chiropr Assoc 1999 (Jun); 43 (2): 75–88 ~ FULL TEXT Stability: from biomechanical concept to chiropractic practice
'물리치료 공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Impingement Syndrome의 정의 (0) | 2022.01.02 |
|---|---|
| Core exercise (bracing) (0) | 2020.10.18 |
| 척추전방전위증(Spondylolisthesis) (0) | 2020.10.04 |
| 어깨(회전근개) 수술후 재활 part 6(Rotator cuff tear repair Protocol Phase4 (12~16weeks)) (0) | 2020.09.07 |
| 어깨(회전근개) 수술후 재활 part 6(Rotator cuff tear repair Protocol Phase3 (8~12weeks)) (0) | 2020.09.06 |