1) pectoralis minor strech

▷ It may indicate that humeral elevation and external rotation to 90 are important components of pectoralis minor stretching
▷ performed bilaterally streching, which may be more effective prevent trunk rotation toward the side of the stretch, because of this mechanical block
2) posterior capsule stretch (sleeper strech)

3) Latissimus dorsi strech

4) Thoracic mobility exercise
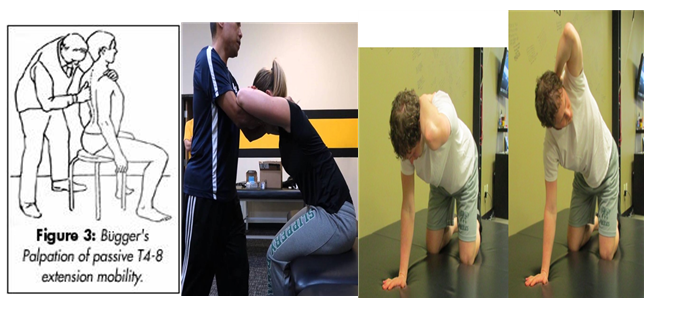
# Effect of posture on pain and ROM
Thoracic kyphosis may not be an important contributor to the devepopment of shoulder pain. While there is evidence that reducing thoracic kyphosis facilitates greater shoudler ROM
5) Shoulder muscle exercise


▷ Conservative, Post OP treatment
large to massive tear, delay postop treatment
Impingement, early postop strengthening
6) Deltoid, Pectoralis, and Latissimus dorsi in large and massive RC tear
▷ in mRCT, The PM and LD muscles are effective in improving glenohumeral kinematics and reducing acromiohumeral pressures
▷ Increased activation of the latissimus dorsi and teres major muscles is an attempt to compensate for the deficient rotator cuff
▷ Humeral head deprssor exercises (pectoralis major and latissimus dorsi)
▷ Deltoid rehabilitation program is suitable for elderly patients with massive rotator cuff tears
7) OKC strengthening exercise


8) more effect isolates position of supra from deltoid

▷ 30 of abduction, mild ER, and 30 of flexion
9) posterior capsular stretch VS capsular stretch + mobilization
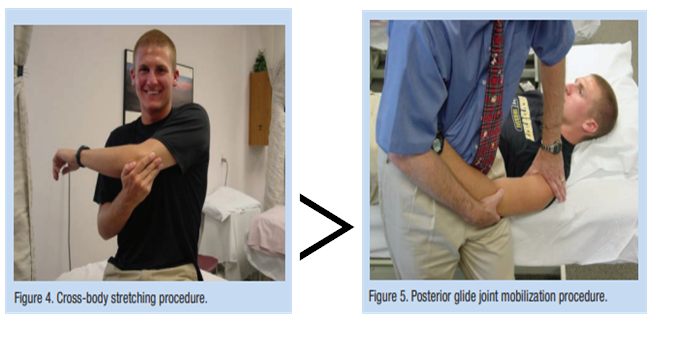
▷ Combination of the cross-arm stretch plus joint mobilization may be an even more effective method for treatment of posterior shoudler tightness.
10) Posterior mobilization
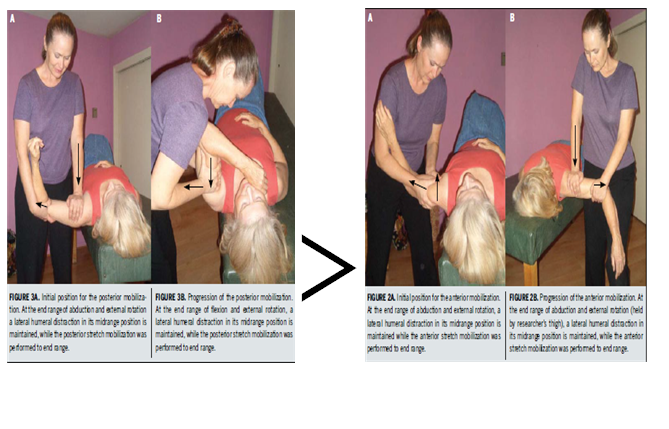
11) Effective position in inferior mobilization

▷ Maximal inferior translation with minimal force was found when a grade 3 mobilization was performed in the OPP
12) Mobilization with movement (MWM)

▷ Effects of Mobilization With Movement on Pain and Range of Motion in Patients With Unilateral Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Reference
The lat length test ELEATE SPORTS ACADEMY
Musculoskeletal Evidence based Treatment
Morrey BF, An KN (1990) Biomechanics of the shoulder. In: Rockwood CR, Matsen FA (ed) The shoulder. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 208–245Google Scholar.
lippitt. clin orthop relat res (1993) Rotator Cuff Tears: causes of shoulder pain: Stabilizing effect of negative intraarticular pressure
L. Kessel, M. Watson Published 1 May 1977 Medicine The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume The painful arc syndrome. Clinical classification as a guide to management.
Rotsalai Kanlayanaphotporn, Ph.D. (Health Sciences), M.Appl.Sc. (Physiotherapy), B.Sc. (Physical Therapy) Published:November 04, 2013 Changes in sitting posture affect shoulder range of motion
Sally Raine, PhD, Lance T. Twomey, PhD Head and Shoulder Posture Variations in 160 Asymptomatic Women and Men
Raine S, Twomey LT. Head and shoulder posture variations in 160 asymptomatic women and men. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1997;78:1215-23.
Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy Published Online:July 1, 2004 Electromyographic Analysis of the Rotator Cuff and Deltoid Musculature During Common Shoulder External Rotation Exercises
P. Chalmers, G. Cvetanovich, +5 authors G. Nicholson Published 1 February 2016 Medicine Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. The champagne toast position isolates the supraspinatus better than the Jobe test: an electromyographic study of shoulder physical examination tests.
Andrea J Johnson 1, Joseph J Godges, Grenith J Zimmerman, Leroy L Ounanian The effect of anterior versus posterior glide joint mobilization on external rotation range of motion in patients with shoulder adhesive capsulitis DOI: 10.2519/jospt.2007.2307
Robert C. Manske, PT, DPT*, Matt Meschke, DO, Andrew Porter, DO, Barbara Smith, PhD, PT, Michael Reiman, PT, DPTFirst Published December 22, 2009 A Randomized Controlled Single-Blinded Comparison of Stretching Versus Stretching and Joint Mobilization for Posterior Shoulder Tightness Measured by Internal Rotation Motion Loss
Choo Yeonki, PT, Ph.D Dept. of Rehabilitation Therapy, Guposungshim Hospital, Manager Effects of Mobilization with Movement Combined with Exercise(EMWM) on ADH, ROM and Functional Performance in Patients with Impingement Syndrome of the Shoulder
The effect of shoulder position on inferior glenohumeral mobilization Dexter W. Witt DHS, DPT, MHS, PT, OCS, FAAOMPT *, Nancy R. Talbott PhD, MS, PT, RMSK
Effects of Mobilization With Movement on Pain and Range of Motion in Patients With Unilateral Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Author links open overlay panelJosé A.Delgado-GilPTaEvaPrado-RoblesOTbDaiana P.Rodrigues-de-SouzaPT, MsCcJoshua A.ClelandPT, PhDdCésarFernández-de-las-PeñasPT, PhDeFranciscoAlburquerque-SendínPT, PhDf
'물리치료 공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 4. Impingement Syndrome의 이학적 검사 (0) | 2022.01.06 |
|---|---|
| Impingement Syndrome의 정의 (0) | 2022.01.02 |
| Core exercise (bracing) (0) | 2020.10.18 |
| Core (0) | 2020.10.18 |
| 척추전방전위증(Spondylolisthesis) (0) | 2020.10.04 |




































